Image Similarity Learning with Siamese Network - Totally-Looks-Like challenge
Totally-Looks-Like challenge can be used to evaluate human-like perception of images. This task is based on https://www.reddit.com/r/totallylookslike/, where users share pairs of images of things that they think look similar.
In this task, one image is taken from a Totally-Looks-Like pair as input and its match will be selected from a list of possible candidates. It is a challenging task because these image pairs are semantically unrelated but visually similar, they might contain similar colours, shapes, textures, poses, or facial expressions, and sometimes only part of the image is relevant to the comparison.
To solve this task, I proposed two methods: Siamese Network with a triplet loss; Siamese Network with a contrastive loss, achieving 83% and 84% accuracy.
Siamese Network with a contrastive loss
Siamese networks are neural networks that contains multiple identical sub-networks, and these sub-networks share the same architecture and weights. Each sub-network processes a different input and produces an embedding vector for further training. And the reason why we choose the Siamese network is that it has proven to be particularly helpful in supervised similarity learning for the small dataset.
Classification Task
If we view the problem as a classification task, we can calculate the probability of the image pair being the Totally-Looks-Like image pair. During the training stage, we label the TLL image pairs as 1 and other random matched image pairs as 0, and then train the neural network to identify the real image pair.
Network Architecture
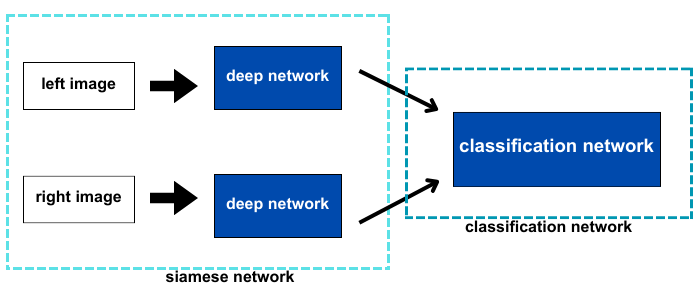
Contrastive loss tries to minimize the distance when images are from the same class but maximizes the distance otherwise. It takes three inputs: “left” image (x1), “right” image (x2) and label (y), and the 0 or 1 label indicates whether the images are from the same class. The contrastive loss function is defined as:
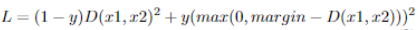
I combine the Siamese network and the classification network into a full network and use contrastive loss as the loss function. The inputs of the Siamese network are extracted features from the pretrained model, after processed by the deep network, the outputs of the Siamese network are then used as the inputs of the classification network. The classification network then returns the probability of the image pair being Totally-Looks-Like image pair. In this model, the deep network is a fully-connected laye
Siamese Network with a triplet loss
Image Retrieval Task
If we involve the challenge in an image retrieval task, we can calculate the similarity between the “left” image and the “right” candidate image, so the higher similarity indicates the candidate image is more likely to be the ground truth image.
Network Architecture
 S. Das, “Image similarity using Triplet Loss,” Medium, Jul. 23, 2019. https://towardsdatascience.com/image-similarity-using-triplet-loss-3744c0f67973
S. Das, “Image similarity using Triplet Loss,” Medium, Jul. 23, 2019. https://towardsdatascience.com/image-similarity-using-triplet-loss-3744c0f67973
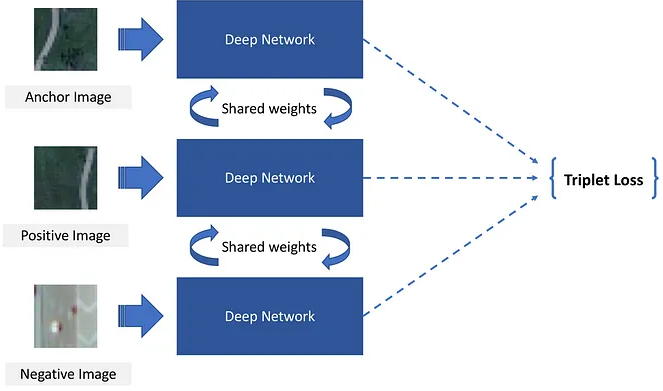
Triplet loss is a distance based loss function, it takes three inputs: anchor image (a), positive image (p) and negative image (n), and aims to minimize the distance between the same class images while maximizing the distance between the images from different classes. The anchor image and the positive image are from the same class, while the negative image is from a different class. The triplet loss function is defined as:
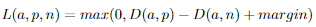
D(x, y) is the distance between x and y, and often implements L2 distance or (1 - cosine similarity).
I first extract the features of the images from the pretrained model as the inputs of the Siamese network. Then in the deep network part, I simply add a fully-connected layer to reduce the input by half. And the outputs of the deep network are used to calculate the triplet loss.
Therefore, the deep network is trained to produce the prefect representation of the images for similarity learning. During the prediction stage, Is can simply calculate the cosine similarity between the deep network outputs of different images, and treat it as the probability of the image pair being Totally-Looks-Like image pair.
Implementations
For both implementations, I choose clip model as the pretrained model, obtain the features of all the images from clip model and save as npy files for further use.
Triplet loss
To construct the training dataset, for each TLL image pair I randomly select 19 images from the “right” images as the negative images. Then integer values are assigned to each image as the class label. After the training, I use the outputs of Siamese network to calculate cosine similarity.
Contrastive loss
For contrastive loss, I use the same “right” images from triple loss to construct image pairs. And for each image pair, 0 or 1 are assigned to indicate if it is the TLL image pair. For the prediction, I use the output of the full network as the predicted probability.
Evaluation
The results are evaluated by top2-accuracy, where the images with top 2 highest probability are compared to the ground truth image, and if any of them matches then the prediction is scored correct.
Triplet loss
-
I use the output of the Siamese network to calculate cosine similarity: 0.828.
-
I add a classification network which takes the outputs of the Siamese network as inputs. And the classification network is the same full network from Siamese network with a contrastive loss in the method section: 0.793
-
I remove the deep network part from the classification network, meaning the outputs of the Siamese network with the triplet loss are directly used for probability calculation: 0.822
The trained Siamese network with a triplet loss can give a good representation of the images. By simply calculating the distance between two images with the new embeddings, the top2-accuracy is around 83%. So when I add another classification network, the model is more prone to overfitting, which explains why the top2-accuracy gets lower in the second and the third experiment.
Contrastive loss
-
I didn’t add the deep network at first: 0.616.
-
I add the deep network: 0.81
-
I test 3 different pretrained models: clip_rn50x4, clip_rn101 and clip_vitb32. And clip_rn50x4 has the best performance. So with clip_rn50x4 as the pretrained model, I further explore the effects of different epochs. By setting the training epoch to 2, 3, 4, 5, the model has the highest score with 4 epochs.
-
I replace the global visual features with the local grid features: 0.693
-
I concatenate the local grid features and the global visual features as the inputs of the model: 0.686
Conclusion
With the clip_rn50x4 model as the pretrained model and 4 training epochs, the trained Siamese network with a contrastive loss gives the highest score by far. However, if I change the model input from global visual features to local grid features or concatenate them, the scores decrease by almost 15%. Unlike other image retrieval tasks or classification tasks, the similarity of the TLL image pair is based on the high level perception instead of the low level local features like color, shape and texture. So with the local grid features, the model fails to learn the high level global perception of the images, leading to the bad model performance.
I also try to put the clip_rn50x4 model in the deep network, so the network can directly update the weights of the clip_rn50x4 model. However, the model can’t finish one epoch training within 18 hours, so I give up this idea.
Error Analysis
 correct precdition
correct precdition
 wrong precdition
wrong precdition
Visual results of Siamese network with a triplet loss: the first image is the “left” images, other three images are the “right” images of top3-highest probabilities, the image in the red square is the ground truth image
The model is able to give the correct prediction, even though the color and the text of the image pair are different. However, about the wrong prediction, the model predicts other two candidate images have the higher probabilities. As “qyx” and “opv” images have the similar hairstyle and facial expression to the “left” image, it means the model can capture the high level global features. But the model might ignore some low level local features like the texture, since the “fhp” image looks like the “left” image in the way that the objects share similar wrinkled texture. Thus, to improve the model performance, I need to consider adding the local features into the model.